Supplementing with Collagen has been popular in the past 10 years. Apart from its medical benefits, collagen has become popular because of its perceived ability to keep skin smooth and young-looking. It has been used as a skin filler in the 1980s. Recently, it has been advertised as a supplement powder added to smoothies or coffee by celebrities like Kourtney Kardashian and Jennifer Anniston.
One of the most abundant proteins in the human body is collagen. In fact, 75% of the skin’s dry weight is collagen. It accounts for 30% of our body’s total protein mass. According to Dermatologist Whitney Bowe (as cited by WebMD), collagen acts as a “glue that holds the body together”. As a matter of fact, the term comes from the Greek word “kola” meaning glue. However, the human body produces less and less collagen as we age.
DEFINITION
Collagen is basically made up of a triple helix of amino acids that forms a fiber-like structure. Primarily, a collagen molecule has glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline.
Our body produces collagen naturally. Similar to other mammals, humans require collagen to keep the elasticity of our skin, strengthen our muscles and bones, and provide structure to our cells.
TYPES OF COLLAGEN
At present, there are 29 types of collagen. The human body mostly has Types I, II, and III.
Type I – Known as the longest collagen chain. It is abundant in our skin, blood vessels, bones, and muscles.
Type II – A peptide that contains chondroitin and glucosamine. It is the main protein in our cartilages.
Type III – It is the dominant collagen in our soft tissues. This type of collagen is in our hollow organs like the heart, digestive tract, and blood vessels. It is also a protein common in wound healing.

BENEFITS OF COLLAGEN
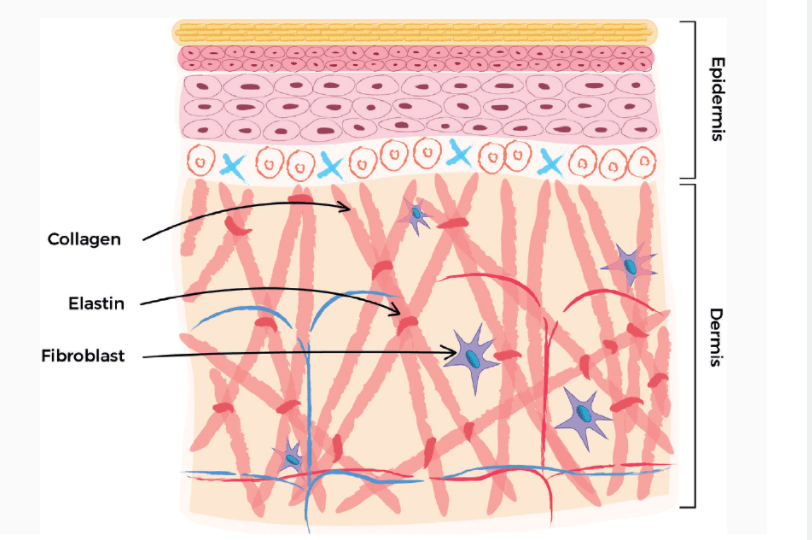
1. Collagen Reduce Skin Aging
Collagen is a protein produced by fibroblast in the dermis of human skin, responsible for skin texture and shape. Elastin, which is found in the connective tissues, along with collagen, provides skin its elasticity. The production of collagen naturally declines by 1% by 25 years old. Adding hydrolyzed collagen peptides can repair skin aging caused by UV rays. Supplementing with hydrolyzed collagen improves skin elasticity and hydration according to research and personal anecdotes.
Intrafibrillar (green colored image) spaces of collagen matrices
2. Improve Bone Density
Taking collagen supplements can reduce and prevent osteoporosis, especially among women. Mainly, collagen reinforces the bone by making it denser or less porous. As a result, bones become less brittle. Collagen supplements can also aid in bone healing.
Collagen is also found in bone-support structures like ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Supplementing with collagen peptides or taking collagen-rich food is important to maintain healthy bones and joints.
decrease body fat
3. Promote Weight loss
Collagen peptides can increase satiety or feeling “full”. As a result, it helps you feel less hungry. Since it also has few calories, you can add it to your morning drink or smoothie. Also, having high-protein meals reduce blood sugar spikes.
Collagen supplements can also reduce fat accumulation according to some studies. However, they used Skate collagen peptides (from fish), in these studies.
4. Grow Muscles
Do you know that about 10% of our muscle tissues is collagen? Collagen has glycine and arginine, which are the main component of creatine. Since creatine strengthens and builds new muscle fibers, adding collagen after workouts aid muscle growth.
HYDROLIZED COLLAGEN PEPTIDES
As mentioned above, apart from supplementing with collagen, our body creates collagen naturally. However, as we age, the production of collagen also deteriorates. As a result, our skin becomes thinner, less elastic, drier, and starts to form lines, wrinkles, and stretch marks. I know because it starts happening to me when I turned 32. Out of nowhere, deep dark stretch marks formed on my thighs and there were no creams that could reverse it (yet). Apart from the skin, collagen depletion also affects our joints, hair, bones, and muscles.
There are also other reasons or factors for the decline of collagen. As we get older, our stress levels and UV exposure also increase. Some become more exposed to smoking, which decreases oxygen in the cells. Moreover, having a busier lifestyle may lead to inflammatory diets, which are high in sugar, processed food, alcohol, and fried foods.
To counter the loss of collagen, we can increase our collagen and protein from food intake –such as adding gelatin or bone broth. When protein and collagen reach our digestive tract, our body breaks them into amino acids. Afterward, the body will put together or synthesize glycine and proline to form collagen. By adding protein and collagen-rich food, we are giving our body a sufficient supply of the essential amino acids to improve collagen formation.
However, since the reason for age-related collagen decline is the body’s lower ability to process collagen, supplementing with collagen can help. Through the process called hydrolysis, water molecules break the collagen into short-chain amino acids or collagen peptides. Since peptides are smaller and soluble in water, they can be absorbed by our gastrointestinal tract better. These peptides stimulate the production of collagen and protect against the degradation of our collagen supply. You can start supplementing collagen peptides from different sources -depending on your preferences and requirements.
Collagen Peptides Sources
Bovine Collagen – The bovine species include buffalos, cows, yaks, bison, antelope, etc. Bovine collagen is derived from boiling their hides, bones, tendons, cartilages, and other connective tissues. Often it comes from grass-fed and pasture-raised cattle. If the collagen comes from bovine, it includes both type I and type III.
Marine Collagen – When we say “marine.” we refer to collagen derived from fish skin and scales. Most of the fish used are wild-caught Spanish mackerel, Cod, or Pollock. Some marine peptides are from fresh-water Tilapia and Pangasius. This type of collagen has Type I peptides, thus it is popular in the beauty industry.
Porcine Collagen – Often gelatin comes from pork skin. Porcine collagen comes from the bones and skin of pigs. Gelatin is only partially-hydrolyzed. It does not dissolve in cold water and is less digestible than collagen peptides. Similar to bovine collagen, porcine collagen has type I and type III collagen.
Chicken Collagen – Notably known as UC-II for Type II collagen, hydrolyzed chicken collagen comes from simmering free-range chicken bones, skin, and cartilage. As the prominent source of type II collagen, chicken collagen helps joint pain, arthritis, and surgery recovery.
Vegan Pro-Collagen – Currently genetically modified bacteria and yeast are being bioengineered to produce collagen. However, these types of collagen are not yet available in the market. Instead, they are plant-based collagen promoters, which include ingredients needed by the body to produce collagen.
Algae Pro-Collagen – Another pro-collagen supplement that may have spirulina or chlorella. Algae supplements support collagen production because it has the proteins and minerals required to synthesize collagen. Both contain essential amino acids.
Research on Collagen Supplements
Many still doubt the claimed benefits of supplementing our diets with collagen because most research is industry-backed. However, these researches and personal anecdotes show improvements mostly in skin elasticity and hydration. Personally, I have been seeing positive results on my skin’s suppleness after taking collagen peptides. Below are some of the research on collagen supplements.
A PubMed article on the systemic review of Oral Collagen Supplementation concluded that supplementing with collagen helps in wound healing and skin elasticity. Their findings revealed notable changes within 4 to 8 weeks. Also, the study found no adverse effects from supplementing with collagen.
Bolke and colleagues created a randomized blind study of a drinkable collagen supplement (from Germany). Their research showed a substantial improvement in skin hydration and elasticity among those who took the 2.5g collagen supplement with vitamin C, zinc, vitamin E, biotin, and acerola fruit extract. Interestingly, this study showed that the effect persist even after a month after the study.
Dietary chicken-collagen supplements helped reduce wrinkles among the participants of a double-blind study made by Schwartz, et al., in 2019. The study includes supplementing with 500mg of chicken collagen with chondroitin (100g) and hyaluronic acid (50g).
In a 2020 research by Sangsuwan and Asawanonda, there was a significant improvement of skin elasticity after taking marine collagen supplements for 4 weeks. Similar to the previous studies, the improvements were retained even after 4 weeks of discontinued use.
The most recent was a triple-blind trial, published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology in 2021. The 12-week study includes women aged 45 to 54. It revealed that the intake of marine collagen peptides resulted in a 20% improvement in skin elasticity and 25% better firmness vs placebo.
TOP COLLAGEN SUPPLEMENTS
Most websites suggest collagen supplement powder like Vital Proteins, Thrive Market, and NeoCell. In Southeast Asia, collagen supplements from Japan and Thailand are very popular. Personally, I chose cheaper but good quality products. First, I wanted a collagen supplement in capsule or tablet form, which I can take daily. Second, I want a collagen powder that I can mix with any food or drink. The following are my collagen supplement choices:
Disclosure: I use affiliate links and receive a small commission for purchases made using the links. I only include products that I personally use and like.
Lake Avenue Hydrolyzed Collagen Type I and Type III Capsules with Vitamin C
Apart from being affordable, I like this product because it contains 1 gram of hydrolyzed bovine collagen peptides per capsule. Since it is bovine, it has both type I and type III collagen. It also has Calcium Ascorbate or Vitamin 3, which is a precursor to collagen building. I take this for my daily supply of collagen before bedtime.
Sports Research Collagen Peptides Type I and Type III Powder (unflavored)
I prefer unflavored collagen powder because it has fewer fillers, less sugar, and can be added to coffee and smoothie. I usually add half-scoop on my morning coffee. It does not have a fishy after taste, dissolves easily, and blends well. As for the quality, it also has Type I and Type III, which are perfect for my needs. While 1 full scoop has 11 grams of collagen, I only take half –so that’s 5-6 grams.
Solumeve Collagen Peptides (unflavored)
I have recently purchased this because it is a cheaper alternative. It is consists of bovine collagen, which has Type I and Type III. This is already 1 pound with 46 servings of 10 g of hydrolyzed collagen.
Note that the recommended dosage for improving skin health is 2.5 to 10 grams for 8-12 weeks. Also, if we take too much collagen, our body will break it into amino acids. The body will synthesize it into protein types that the body needs. Since I am doing simple workouts and drinking a protein shake every afternoon, I try to take collagen after breakfast (when I have already digested breakfast) and at night (when my body has absorbed whey protein). As much as possible, I want my collagen supplements to be for collagen repairs.
Additionally, I am still in my early 30s. I believe that my body can still manufacture enough collagen. Thus, I am not looking for heavyweight supplements. However, I am considering taking the full scoop of SR collagen powder when I am in my late 30s. Then, I might switch to Vital Proteins in my 40s or something better.
Also, I will be trying some Japanese collagen supplements soon. My sister will be sending me some. I will update this article in 3-4 months.
Now, if you are still in your 20s or just anxious about supplements, you can instead try natural sources of collagen.
FOOD SOURCES
Bone Broth – Brewing and simmering bones and skin of chicken, pig, or cow with a little vinegar and some spices have been traditional for making broth for soups. In some countries, they also add chicken feet to their soups (which is a good source of Type II collagen).
Fish – Frying fish skin is the best way to enjoy marine collagen. Fish skin has type I collagen, which is the easiest to digest. At home, we often have fried Tilapia and Milkfish.
Eggs – Both the egg whites and egg yolks have collagen. Eggs are good sources of protein in general. One egg already has 6g of proteins. Whenever I need more protein in my diet, I add some eggs to my meals. Because of its high protein content, it can act as a procollagen. The egg whites have glycine and proline, which are the building blocks of collagen.
Gelatin – In itself, gelatin is collagen. Often it is included in food, but more commonly used in making desserts.
Algae – Adding Chlorella and Spirulina to your meals, smoothie, or diet can also boost collagen production. However, they do not have collagen in themselves.
HEALTHY HABITS
Limit Caffeine – Caffeine only limits the production of collagen, not destroys it. Caffeine negatively affects the skin and promotes its aging process. As I have mentioned, I add collagen to my morning coffee –but to clarify I am drinking decaf. Note that there’s only 2 to 7 mg of caffeine in decaf, while regular coffee has more or less 80 to 100 mg.
Reduce Sugar – Sugar, when unused by the body, can destroy collagen. Excess blood sugar can break down collagen through a process called glycation. Moreover, it can change the stable type III collagen to a more fragile type I. Consider having only up to 200 calories of carbs and sugar in your diet per day.
Increase Antioxidants – Being exposed to free radicals that are released from fried foods, sun exposures, inflammation, etc., will increase aging. To combat free radicals, you can increase your antioxidants by eating berries and other fruits (apples, grapes lemon), nuts (walnut, pecans), spices (turmeric, cinnamon, cumin, clove), and vegetables (carrots, onions, garlic, peppers, broccoli, tomatoes). Even coffee, tea, and cocoa have antioxidants that can help our skin repair itself.
Avoid the Sun – Even if you are staying at home, try to protect your skin with SPF 30.
Exercise More – Of course, the list is incomplete without exercise. Exercising improves blood circulation, which improves the oxygen and nutrients distribution in the body and flushes out toxins.
Better Sleep – Collagen is produced while our skin regenerates. The process of cell regeneration happens more quickly at night. This is how “beauty sleep” became popular. Our skin recovers better when we are sleeping, whereas we get dry dull skin when we are sleep-deprived. Lack of sleep deter collagen production, activates oil glands due to cortisol, and reduces the skin’s efficiency to remove toxins and repair.
TAKEAWAY
Collagen is naturally produced by the body. It is the most abundant protein found in our skin, bones, joints, muscles, and connective tissues. Collagen is fibers made up of amino acids –mainly glycine and proline. Nonetheless, aging slows down the regeneration of cells and increases inflammation, resulting in a decrease in collagen production. Therefore, collagen supplements may help augment the loss of collagen, maintain skin elasticity, improve bone density, promote weight loss, and strengthen our muscles. We can also incorporate healthy habits like limiting caffeine, exercising, consuming antioxidants, and having better sleep to help our body restore its collagen levels.











Your blog post had me hooked from the first sentence.